Global 8D – D5: Choose and Verify Permanent Corrective Action (PCA)

Having determined the root cause/s of the problem and the escape point you are now in a position to determine and choose the most appropriate Permanent Corrective Action (PCA).
PCA’s need to be considered for both the root cause and the escape point.
The PCA needs to meet several requirements that satisfy both customer and business needs. Given that there may be a number of possible permanent corrective actions that may be applied, I will describe how the most appropriate PCA is arrived at.
The process for determining the possilbe PCA's will be driven by the nature of the root cuases and the business objectives.
The final choice of which PCA's to implement will be determined from:
-
The best interest of the customer
-
The needs of the business
Define Permanent Corrective Actions
Having identified the root cause of the problem under investigation, the team will have the data and information at hand to determine what corrective action options there might be available to implement. These are all considered and articulated in such a ways as to ensure that all the necessary steps needed to remove and protect against the route cause have been considered.
As stated above, the process for determining the possilbe PCA's will be driven by the nature of the root cuases and the business objectives.
Chose The Permanent Corrective Action
For this activity we will consider two levels of needs:
-
Givens – those criterion that must be met (mandatory) and that are measureable and realistic to achieve and satisfy both customer and business needs
-
Wants – those criterion that are nice to have but not necessarily critical and also cover both customer and business aspirations
Examples
Givens could be:
-
Must be implemented within three months
-
Must not cost more than £25,000 to set up
-
Must be able to continue delivering product during implementation
-
Must solve the root cause of the problem permanently
Wants could be:
-
To be cost effective in the first year of operation (Set up costs plus running costs within the first year)
-
To be introduced as soon as possible
-
To be implemented without overtime
-
To have zero impact on energy consumption
-
To work on both lines simultaneously
There are two worksheets that are used in this process, the Criteria Worksheet and the Decision Making Worksheets.
Criteria Worksheet
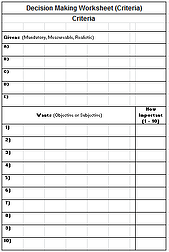
Using the Criteria Worksheet on the right, the Wants are scored in terms of relative importance, 10 being the highest. This score will be used as part of the "choosing" process.
The Givens are not scored, these are things that must be achieved by the PCA
This is worksheet used for recording the givens and wants. These are normally populated by the business management team.
A copy of this can also be downloaded free, accessed via a 'button' at the end of this article.
Decision Making Worksheet
Having established the Givens and Wants, you can now rank each proposed PCA against these criteria. To help this process we use the Decision Making Worksheet.
NOTE: the number of Givens and Wants worksheets used will depend upon the number of proposed PCA's. One complete section must be recorded for each proposed PCA
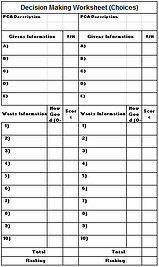
The Decision Making Worksheets are used to rank each of the PCA’s by first determining if the PCA meets all of the givens.
If the PCA does not meet all of the givens, then it cannot be progressed in its current form.
Then the wants are scored as to how well the PCA achieves each criteria.10 is completely and 0 is not at all.
The scores are added up to and this summative score is used to rank the PCA’s
The highest scoring PCA option is normally the one chosen to move forward with.
Verify The Chosen PCA
Before the PCA is fully confirmed, the Global 8D team need to verify that the PVA will actually meet all of the givens and the wants are achieved at the level declared in the decision making worksheets
The Team must verify that the PCA will eliminate the root cause permanently for both the root cause and the escape point.
When verification testing is carried out, it is critical to remeber that an Interim Containment Action has been put in place. Verification must be carried out in such a way that there is no influence on the outcome of verification testing. e.g remove the ICA for testing purposes.
Complete The G8D Form (Template)
Complete the Global 8D form and circulate. Remember to update team composition for any changes that are made at the end of this stage.
The G8D form is a summary of the problem solving activity and is suppoirted by all of the other worksheets, data and supporting information. At this stage the report should include the decision making worksheets, verification testing process and data generated as a results of the problem solving activity.
Graham Cripps
Results Consortium Ltd